Home
Andriod
IOS
Windows
BlackBerry
Contact us
Home
Andriod
IOS
Windows
BlackBerry
Contact us

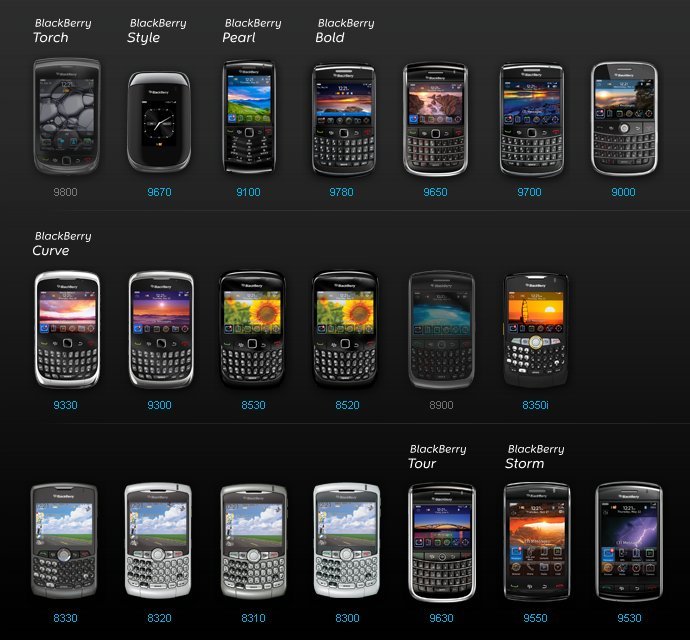
BlackBerry is a brand of smartphones, tablets, and services originally designed and marketed by Canadian company BlackBerry Limited (formerly known as Research In Motion, or RIM).[1] Beginning in 2016, BlackBerry Limited licensed third party companies to design, manufacture, and market smartphones under the BlackBerry brand. The original licensors were BB Merah Putih for the Indonesian market, Optiemus Infracom for the South Asian market, and BlackBerry Mobile (a trade name of TCL Technology) for all other markets.[2][3] Texas-based startup OnwardMobility acquired a license to develop 5G devices for the enterprise market with manufacturing partner FIH Mobile beginning in 2021.
BlackBerry was one of the most prominent smartphone brands in the world, specializing in secure communications and mobile productivity, and well known for the keyboards on most of its devices. At its peak in September 2013, there were 85 million BlackBerry subscribers worldwide.[4][5] However, BlackBerry lost its dominant position in the market due to the success of the Android and iOS platforms; its numbers had fallen to 23 million in March 2016.
Research in Motion (RIM), founded in Waterloo, Ontario, first developed the Inter@ctive Pager 900, announced on September 18, 1996. The Inter@ctive Pager 900 was a clamshell-type device that allowed two-way paging.[13] After the success of the 900, the Inter@ctive Pager 800 was created for IBM, which bought US$10 million worth of them on February 4, 1998.[14] The next device to be released was the Inter@ctive Pager 950, on August 26, 1998. The very first device to carry the BlackBerry name was the BlackBerry 850, an email pager, released January 19, 1999. Although identical in appearance to the 950, the 850 was the first device to integrate email and the name Inter@ctive Pager was no longer used to brand the device. The first BlackBerry device, the 850, was introduced in 1999 as a two-way pager in Munich, Germany.[15] The name BlackBerry was coined by the marketing company Lexicon Branding. The name was chosen due to the resemblance of the keyboard's buttons to that of the drupelets that compose the blackberry fruit.[16] The original BlackBerry devices, the RIM 850 and 857, used the DataTAC network. In 2002, the more commonly known convergent smartphone BlackBerry was released, which supports push email, mobile telephone, text messaging, Internet faxing, Web browsing and other wireless information services.[17] BlackBerry gained market share in the mobile industry by concentrating on email. BlackBerry began to offer email service on non-BlackBerry devices, such as the Palm Treo, through the proprietary BlackBerry Connect software.


Mihal "Mike" Lazaridis is a Greek-Canadian businessman, investor in quantum computing technologies, and founder of BlackBerry, which created and manufactured the BlackBerry wireless handheld device. Lazaridis served in various positions including Co-Chairman and Co-CEO of BlackBerry from 1984 to 2012 and Board Vice Chair and Chair of the Innovation Committee from 2012 to 2013. As a passionate advocate for the power of basic science to improve and transform the world,[4] he co-founded Quantum Valley Investments in March 2013 with childhood friend and BlackBerry co-founder Douglas Fregin to provide financial and intellectual capital for the further development and commercialization of breakthroughs in quantum information science.[5] In 1999 he founded Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics, where he also serves as Board Chair.[6] In 2002, he founded the Institute for Quantum Computing.[7] He is also a former chancellor of the University of Waterloo, and an Officer of the Order of Canada. With an estimated net worth of US$800 million (as of June 2011), Lazaridis was ranked by Forbes as the 17th wealthiest Canadian and 651st in the world.[8]
-->>More About Inventer IN wikipedia<--
Douglas Fregin is a Canadian businessman who co-founded BlackBerry Limited (then called Research In Motion) in 1984. Fregin acted as vice-president of operations until his retirement in 2007
-->>More About Inventer IN wikipedia<--